
Calculating retained earnings after a stock dividend involves a few extra steps to figure out the actual amount of dividends you’ll be distributing. For someone studying a company’s financials, they might need more than just looking at the total amount of money saved in a quarter Outsource Invoicing or year to give them a clear picture. It’s better to track this over a few years to see how much they’ve saved.
What Is Included in Stockholders’ Equity?
There are times when company owners must invest their own retained earnings on balance sheet money into the company. Long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, are typically mortgages or loans used to purchase or maintain fixed assets, and are paid off in years instead of months. Even if they may be used to purchase assets, retained gains are not assets in and of themselves. Retained earnings can be a liability for a corporation since they are put aside to pay investors in the case of a company sale or buyout.
- Subsequently, you would not list them as an asset but as liabilities on a specific balance sheet.
- Management, having better knowledge of the market and the company’s operations, may have ambitious plans for future growth that will yield substantial returns down the road.
- They are cumulative earnings that represent what is leftover after you have paid expenses and dividends to your business’s shareholders or owners.
- Many companies consider dividend payouts and plan investment strategies at year end.
- If depreciation expense is known, capital expenditure can be calculated and included as a cash outflow under cash flow from investing in the cash flow statement.
What is the difference between retained earnings and revenue?

Demerits of Retained Earnings Because business profits fluctuate from time to time, it is an uncertain source of funds. Excessive retained earnings cause shareholder dissatisfaction because it reduces the dividends payable to them. Reserves may be overcapitalised as a result of frequent capitalisation.
Where Is Retained Earnings on a Balance Sheet?

Higher dividend payouts reduce retained earnings, limiting funds available for growth or debt reduction. Lower dividends increase retained earnings but may disappoint investors seeking regular income. A stable dividend policy involves paying a consistent dividend per share, which appeals to income-focused investors. Under this approach, retained earnings fluctuate based on the difference between net income and dividend payments. Companies strive to maintain dividend stability even when profits vary. It is essential to distinguish retained earnings from cash flow, as they represent different financial concepts.

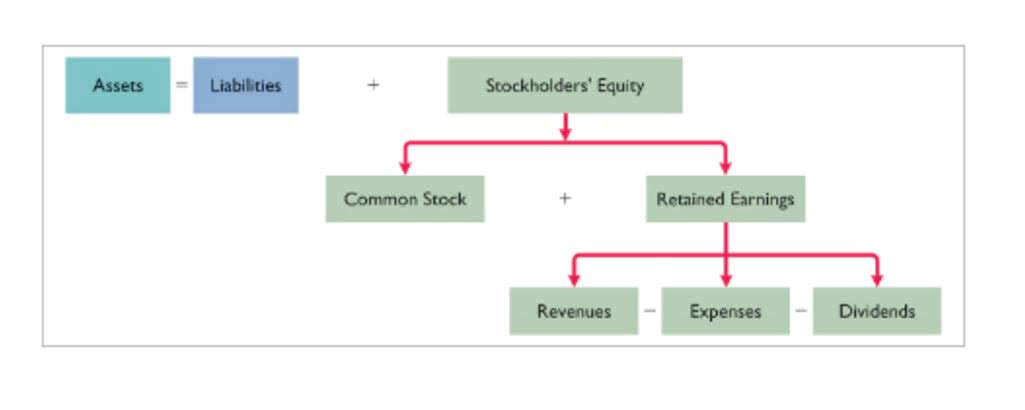
Also, keep in mind that the equation you use to get shareholders’ equity is the same you use to get your working capital. It’s a measure of the resources your small business has at its disposal to fund day-to-day operations. Your company’s balance sheet may include a shareholders’ equity section. This line item reports the net value of the company—how much your company is worth if you decide to liquidate all your assets. Now your business is taking off and you’re starting to make a healthy profit which means it’s time to pay dividends. Retained earnings are referred to as that part of earnings or profit that is not distributed to the shareholders as dividends.
Balance Sheet: Explanation, Components, and Examples
- Retained earnings are a clearer indicator of financial health than a company’s profits because you can have a positive net income but once dividends are paid out, you have a negative cash flow.
- Even though they are not assets in and of themselves, retained earnings may be utilized to acquire equipment, inventories, and other investments.
- As was previously stated, double-entry accounting supports the expanded accounting equation.
- Corporations are separate legal entities from their owners, which means profits belong to the company itself, not directly to the shareholders.
- The Current Assets account is important because it demonstrates a company’s short-term liquidity and ability to pay its short-term obligations.
- This reinvestment into the company aims to achieve even more earnings in the future.
Because retained earnings are a kind of equity, they are included under shareholders’ equity on the balance sheet. Even though they are not assets in and of themselves, retained earnings may be utilized to acquire equipment, inventories, and other investments. Consequently, a firm with a substantial retained earnings balance may be well-positioned to undertake future asset acquisitions or boost dividend payments to shareholders. Now that you know what counts as retained earnings, how do you calculate them? You’ll need to know your previous retained earnings, your net income and the dividends you’ve paid. You should be able to find your previous retained earnings on your balance sheet or statement of gross vs net retained earnings.
Retained earnings are a vital indicator of a company’s financial health and performance. They reflect the cumulative profits retained in the business, which can be used for growth, debt reduction, or other strategic purposes. Companies with increasing retained earnings are typically seen as financially healthy and capable of investing in future opportunities. At the end of each accounting period, net income from the income statement is transferred to the retained earnings account, increasing it when the company is profitable.
Why Do Companies Pay Dividends?
- A balance sheet explains the financial position of a company at a specific point in time and is often used by parties outside of a company to gauge its health.
- Retained earnings is the cumulative amount of earnings since the corporation was formed minus the cumulative amount of dividends that were declared.
- Retained earnings are the net income of a business after dividends have been paid out to shareholders and/or owners.
- Sub-accounts, of course, can be created under any of these five types of accounts.
- It suggests that you put surplus income back into the company wisely, contributing to its sustainable stability and creating opportunities for future growth.
- However, there are several “buckets” and line items that are almost always included in common balance sheets.
If the number for stockholders’ equity is negative, it may warn of impending bankruptcy (particularly if it is due to a high debt load). Stockholders’ equity is the value of a company’s assets left for shareholders after the company pays all of its liabilities. In an accounting cycle, after a trial balance and adjusting and closing entries are completed, and the income statement is generated, we are ready to prepare the Statement of Retained Earnings.




